
Hackers always try to login to the WordPress website by guessing the administrator’s password. One of the most common attacks is human or bot hackers that try to enter your login page by trying various username and password combinations until they get entry. By default, WordPress allows users to try different passwords without restriction, which is also known as brute force. But admin can upgrade their website to add a protective shell to the website’s security.
In this post, I am going to tell you how to limit the WordPress login attempts using a free WordPress limit login attempts plugin. Let’s get to work!
Why should WordPress login attempts be limited?
By default, WordPress does not limit the number of user login attempts. Hacker will use a script to automatically try different password combinations to log in to the website until the password is cracked.
It is to be noted that most legitimate users won’t take more than a few tries to log in to your site. Therefore, you can limit the number of login attempts made in a set amount of time. Any user who goes beyond the set limit can be temporarily or permanently blocked, as a security measure.
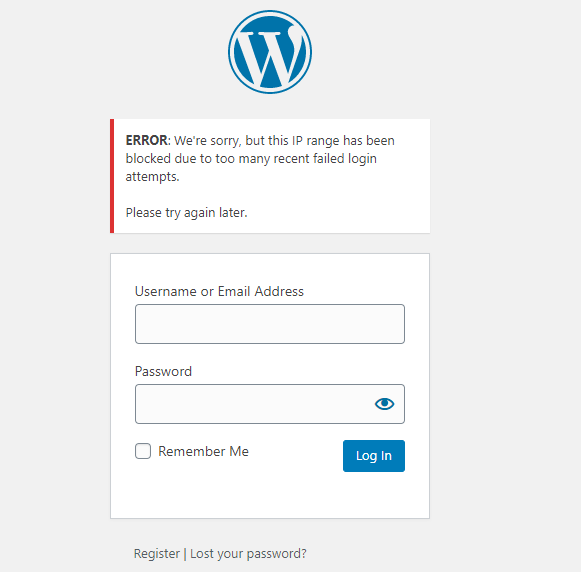
How to limit the number of WordPress login attempts?
A) Using the Free Limit Login Attempts
In order to restrict login attempts, I recommend the Free Limit Login Attempts plugin because it’s 100% free and downloaded over 1 million times up to date.

As soon as it is installed and activated, it starts working. It has also got a variety of configuration options such as the ability to whitelist or blacklist both IPs and usernames by moving on to settings area where you can modify how this functionality works.
In the Statistics section, you will be able to see the number times the plugin locked the login attempts although this section will be empty in the beginning.
Then, under Options, you can decide how many guesses the plugin will allow, the length of time users will be locked out for.
You will be able to see sections labeled Whitelist and Blacklist while scrolling down.
If you add a user to the whitelist or blacklist as you wish. Whitelisted users will be able to log into your site as many times as they’d like whereas blacklisted ones will permanently lock them out.
You should save your changes to this page when you’re done and that’s all you need to do to limit login attempts in WordPress!
B) Using the Login Lockdown Plugin
First, install the Login Lockdown plugin. After enabling it, navigate to the “Settings”-“Login Lockdown” page to configure the plugin.
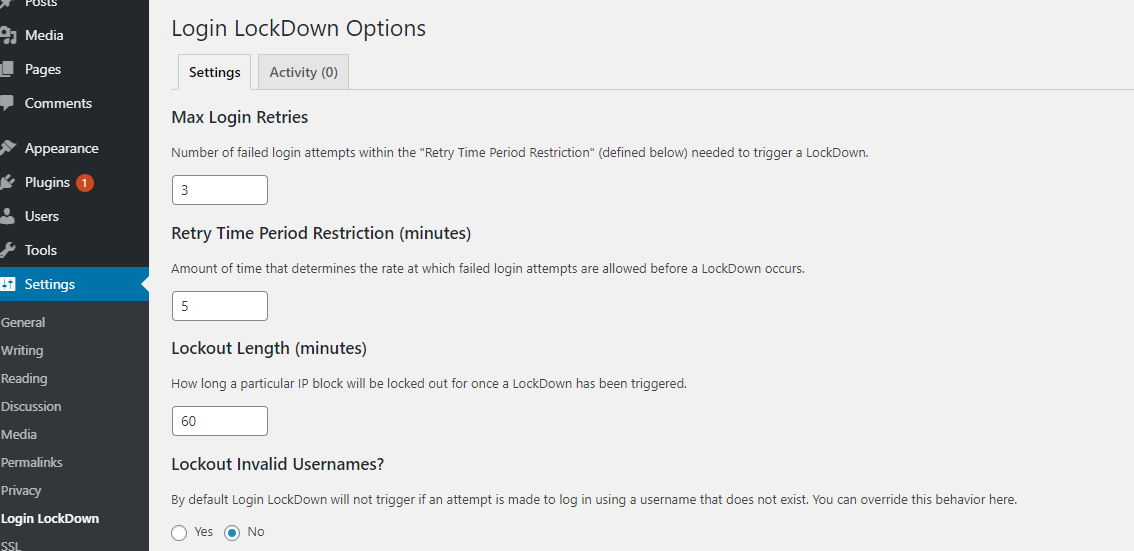
First, define the number of allowed login attempts, and then set how long the user will be locked if the number of failed login attempts exceeds the set value. The lock period of the IP range can also be defined, the default is 60 minutes, it can be adjusted if necessary.
The plugin allows users to try to log in with different invalid usernames. Press “Yes” under “Lockout Invalid Usernames” to stop enabling the behavior.
By default, WordPress will remind users if they have entered an invalid username or password when they fail to log in. Use “Yes” under the “Mask Login Errors” option to block the prompt. Finally, don’t forget to save the settings.
Tips:
The first protection of the website is your password. You should set a strong enough password for your account. You can use some password management tools to help you remember your passwords if you think that strong passwords are difficult to remember.
If your website has multiple authors, then you should enforce strong passwords for users. No website is 100% safe, because hackers can always find new ways to attack your website. So, it is very important to make daily backups of the website. If your WordPress website is an enterprise site, then we strongly recommend that you add a login attempt limit plugin and a firewall to the website, which can effectively prevent brute force cracking and other attacks.





